It’s maths homework time again.
Whoop-dee-doo.
Time to look at some of the weird and wonderful stuff your child’s being taught at school that you’re sure you never needed to know:
1 Number Lines
Certainly in Key Stage 1, children seem to use number lines for everything – adding, taking away, multiplying and dividing. And it doesn’t help that there’s more than one kind of number line, and seemingly countless ways they can be used.
It’s worth getting familiar with number lines; they really help children understand what happens to numbers when they’re learning new types of calculation.

2 Partitioning
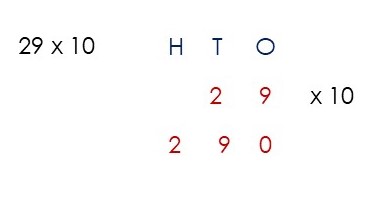
You probably have vague memories of learning about Hundreds, Tens and Units, but you’re sure you didn’t have to break every number down into those place values before adding, or whatever calculation you’d been asked to do.
Why can’t your kids just be taught to put it all in a column, like you did? Much quicker.
Partitioning is really useful when children are getting used to bigger numbers, especially when learning how numbers behave when different kinds of calculation are applied. It’s particularly helpful with mental maths if you understand how each digit is affected by its place value, and it helps with other methods, such as the grid method for multiplication.
Speaking of which …
3 Grid Method (Gridding)
The grid method is particularly helpful for children learning to multiply numbers that are bigger than those they would learn off by heart.
Yes, it takes longer than the traditional long multiplication method, but it does help children (and adults) understand what’s happening within the more formal multiplication methods. A good stepping-stone from informal methods to the more formal method.

4 Chunking
What?
Chunking is a term used in some calculations, such as division, whereby several pieces of information are ‘chunked’ together to make one easy-to-remember piece of information, thus speeding up the calculation process.
For example, when children are learning to use repeated subtraction to understand division:
85 ÷ 5
How many lots of 5 do we need to take away from 85 until there are no 5s left?
Rather than taking away one lot of 5 at a time, they can start by taking away one big ‘chunk’ of 5s:
85 take away ten lots of 5 that’s 85 – 50
which leaves 35
So now you’re left with 35, which is 7 lots of 5
How many lots of 5 in total did you need to take away?
10 lots of 5 add 7 lots of five = 17 lots of 5 There are 17 lots of 5 in 85
So 85 ÷ 5 = 17
5 Multiplying and Dividing by 10, 100 and 1,000
‘Surely you just bung a zero on the end when you multiply by 10?’
That works until you have to multiply a decimal number by 10.
1.5 with a zero on the end gives you 1.50, which is the same as 1.5
And what about dividing by 10 when your number doesn’t have a zero on the end to knock off?
Knowing which way to move the digits depending on whether the number is being multiplied or divided, and knowing how many places to move those digits depending on whether the number is being multiplied or divided by 10, 100 or 1,000, really helps children understand how our base-ten number system works.
And it’s a huge help when they start learning decimals!
Even though some of the methods your child uses to solve calculations may seem strange to you – even a waste of time – be assured that they are useful for understanding how numbers and calculations work.
There are many more explanations for calculation methods here: https://maths4parents.com/c-addition-subtraction-multiplication-division-calculations.html
